
[ad_1]
Assays accessible
Gross pathology
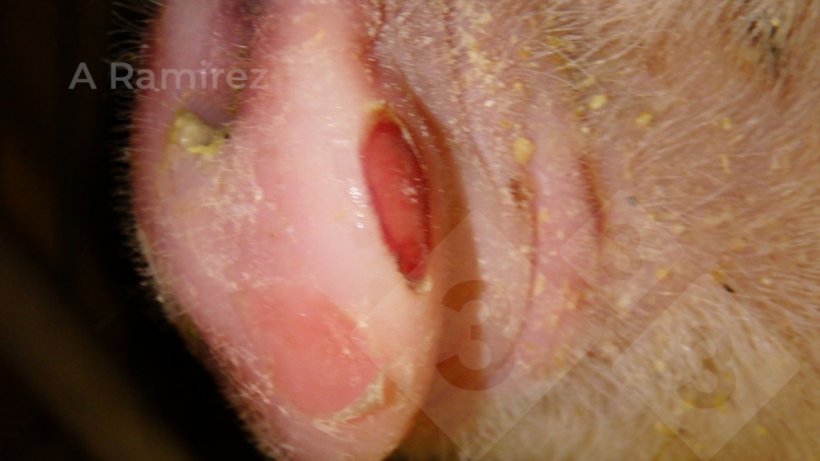
- Identification of lesions particularly vesicles in snout and ft areas
- Professionals:
- Straightforward to establish vesicles grossly
- Cons:
- Clinically indistinguishable from all different vesicular ailments
- Often require different diagnostic affirmation
Polymerase chain response (PCR)

- Detects presence of particular sequence of viral nucleic acid (RNA)
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium (most popular pattern kind), serum, esophageal-pharyngeal pattern (when vesicle or epithelium not accessible), milk
- Professionals:
- Most delicate and most popular technique for detecting agent
- Can typically do pooling of samples to decrease price whereas minimizing lack of sensitivity
- Can goal common proteins for normal detection or serotype particular proteins for serotyping
- Cons:
- Average price
- Requires correct primers particularly if concentrating on structural proteins that are serotype particular
Listing of at present identified serotypes for FMD (There is no such thing as a cross safety between serotypes):
- Asia 1
- South African Kind 1 (SAT 3)
- South African Kind 1 (SAT 2)
- South African Kind 1 (SAT 1)
- C
- A
- O
Antigen Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Ag-ELISA)
- Detects presence of antigen
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium (most popular pattern kind), serum, esophageal-pharyngeal pattern (when vesicle or epithelium not accessible), milk
- Professionals:
- Most popular technique for detection and identification of serotype
- Can be utilized at a person animal or herd degree analysis
- Can be utilized to distinguish serotypes
- Any constructive outcome to wild-type virus is taken into account important
Desk 1. Completely different viral proteins can be utilized to assist with diagnostic objectives.
| Goal antigen | Variability | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Structural proteins | Variable | Serotyping |
| Non-structural proteins | Conserved | Common detection: None-Serotype particular |
- Cons:
- Presence of viral antigen could also be serotype particular
- Might have to do a number of exams to establish serotypes
Antibody Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Ab-ELISA)
- Detects presence of antibodies
- Pattern sorts: serum
- Professionals:
- Circulating antibodies will be detected as quickly as 3-5 days after medical indicators famous
- Animals stay constructive for a number of months
- Can be utilized in older instances
- Can be utilized to distinguish publicity to wild-type from some killed/recombinant vaccines (goal particular non-structural proteins)
- Any constructive outcome to wild-type virus is taken into account important
- Cons:
- Antibody response is serotype particular
- Some animals could keep seropositive for a number of years
- Power of immune response could range with virulence of pressure
- Presence of antibodies doesn’t at all times correlate with safety
Lateral move gadgets (LFD)
- Detects presence of antigen
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium
- Professionals:
- Most popular technique for detection and identification of serotype
- Can be utilized at a person animal or herd degree analysis
- Can be utilized to distinguish serotypes
- Any constructive outcome to wild-type virus is taken into account important
- Cons:
- Presence of viral antigen could also be serotype particular
- Much less delicate than Ag-ELISA
- Might have to do a number of exams to establish serotypes
Virus isolation (VI)
- Isolates dwell virus
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium (most popular pattern kind), serum, esophageal-pharyngeal pattern (when vesicle or epithelium not accessible), milk
- Professionals:
- Conventional gold commonplace
- Isolate virus to be used in vaccine growth (autogenous vaccines) or serology testing (ELISA) to find out serotype.
Cons:
- Costly
- Gradual outcomes
- Requires particular cell strains; bovine (calf) thyroid cells or pig, calf, or lamb kidney cells
- Inoculation course of is labor intensive
- Usually tough to develop (false negatives)
Genetic sequencing
- Sequences virus’s genetic nucleic acids (RNA)
- Pattern sorts: vesicular fluid or epithelium (most popular pattern kind), serum, esophageal-pharyngeal pattern (when vesicle or epithelium not accessible), milk
- Professionals:
- May also help with molecular epidemiology
- Assist establish serotype
- Cons:
- Costly
- Gradual to get outcomes
Outcome interpretation
Gross Lesions (vesicles)
- Constructive: Should examine as attainable FMD
- Adverse: Adverse or missed if testing happens late after an infection or contaminated with a light pressure
PCR
- Constructive: Virus is current
- Adverse: Adverse or virus might have been missed if testing happens late after an infection
Ag-ELISA
- Constructive: Virus is current
- Adverse: Adverse, virus might have been missed if testing happens late after an infection, or examined for fallacious serotype
Ab-ELISA
- Constructive: Maternal antibodies or previous publicity (>2-3 days) to wild-type virus or some vaccines
- Adverse: Adverse or publicity to vaccine or wild-type virus too early to detect, or examined for fallacious serotype antibody
LFD
- Constructive: Virus is current
- Adverse: Adverse, virus might have been missed if testing happens late after an infection, or examined for fallacious serotype
VI

- Constructive: Virus is current
- Adverse: Adverse, virus might have been missed if testing happens late after an infection, or fallacious cell line used
Genetic Sequencing
- Constructive: Virus is current
- Adverse: Adverse, virus might have been missed if testing happens late after an infection, or too little virus current for sequencing
Eventualities
It is very important word that some nations could require approval by federal authorities earlier than any testing for FMD will be executed.
Suspected acute FMD outbreak in any age pigs and herd not vaccinated for FMD
- Accumulate vesicular fluid from a number of affected animals and take a look at by way of Ag-ELISA or PCR; for PCR pattern pooling could also be thought of
Suspected acute FMD outbreak in any age pigs and herd vaccinated for FMD
- Accumulate vesicular fluid from a number of affected animals and take a look at by way of Ag-ELISA or PCR; for PCR pattern pooling could also be thought of
- Accumulate serum from a number of affected animals which have proven medical indicators for at the least 3 days and take a look at individually by way of Ab-ELISA; goal non-structural protein that’s not current in vaccine
Suspicion of FMD circulation in any age pigs with no medical indicators and herd will not be vaccinated for FMD
- Accumulate serum from 30 randomly sampled pigs and take a look at individually by way of Ab-ELISA; goal structural protein
Suspicion of FMD circulation in any age pigs with no medical indicators and herd is vaccinated for FMD
- Accumulate serum from 30 randomly sampled pigs and take a look at individually by way of Ab-ELISA; goal none-structural protein that’s not current in vaccine
[ad_2]