
[ad_1]
The UC Davis Sequence
By: Elina L. Niño
After I first fashioned my lab at UC Davis nearly ten years in the past, as each educational does, I attempted to model myself as a researcher doing X and Y analysis (in my case it was queen well being and reproductive physiology). However the powers that be have determined that I’m really a researcher engaged on X and Y, but additionally Z, Q, W, A, B and C. All joking apart, my analysis targets and lab’s mission have clearly remodeled over time to reply to the multifaceted wants of the California beekeepers with hopes that our findings will profit beekeepers throughout the U.S. and past. If you ask me now what we do, my reply is that the purpose and the mission of the Lab is to additional our understanding of the stressors affecting honey bees, and extra importantly, work in direction of sensible options to assist help beekeepers and honey bee well being. Because of this my staff at any given second works on addressing many points with honey bee pests, pathogens, pesticides, poor diet and extra just lately, environmental stress because of local weather change. And we adore it this manner as a result of there’s all the time one thing new to be taught and discover! In Half 1, we are going to briefly talk about our work on combating that pesky varroa mite and bettering bee well being with supplemental forage plantings and dietary dietary supplements. Half 2 will cowl our work on understanding pesticide impacts in California’s agriculture settings and potential options, we are going to talk about our work on figuring out pollination wants of self-fertile almond varieties, impacts of local weather change and air air pollution on bee well being and wrap up with a examine on improvement of bee sampling methods to assist veterinarians working with beekeepers. So let’s speak about what we’ve been as much as right here within the E. L. Niño Bee Lab.
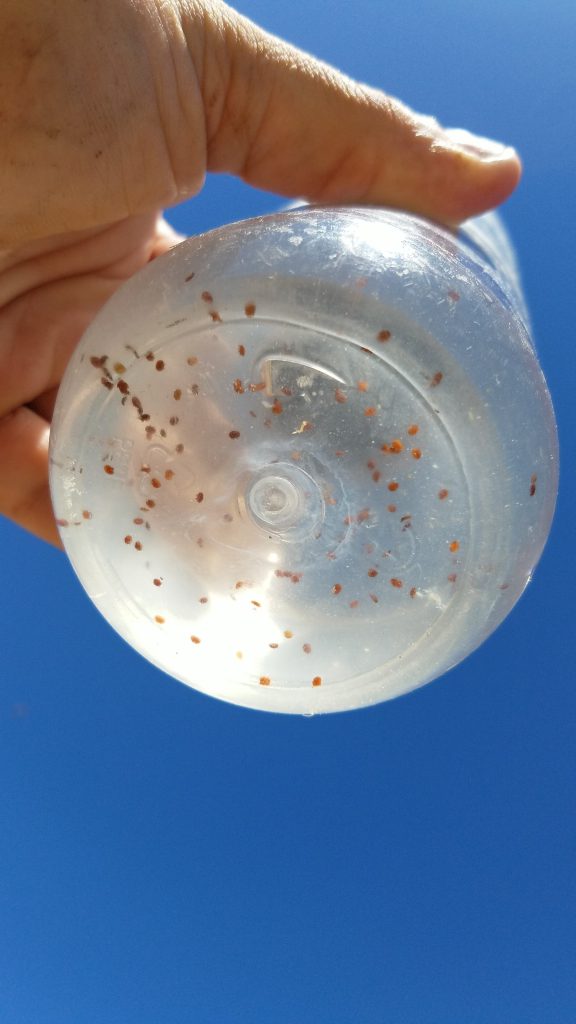

Varroa mite alcohol wash for the management hives within the venture testing varied varroacides. Photograph by B. Nino.
Pests
In all probability the primary query I nonetheless get requested is: “So what do I do about varroa?!” Parasitic varroa mites (Varroa destructor) stay one of many prime stressors beekeepers need to handle of their operations. Because of very elegant analysis by Dr. Samuel Ramsey, now we all know that mites feed on bee fats our bodies, they will transmit detrimental viruses and may suppress immune exercise, making the bees extra weak to different stressors. In brief, they’re very unhealthy information and tough to handle. Sadly, varroa are additionally fairly good at creating resistance to lots of the obtainable miticides. Within the latest previous, my collaborator (Dr. Lambert Kanga from Florida A&M College) and I’ve partnered with the IR-4 Venture to guage and probably develop novel or modified biopesticides for administration of varroa mites. To date, we’ve examined nicely over a dozen completely different compounds together with entomopathogenic fungi, important oils, natural acids, bacteriophages (an experience of Dr. Julianne Grose, Brigham Younger College), and many others.
What have we discovered to this point? Properly, it is rather sophisticated and time consuming to convey a completely developed and efficient product to market, and there are numerous challenges dealing with researchers trying to take action. Keep in mind, we had been simply evaluating merchandise in nearly a last part so you’ll be able to solely think about the challenges which might be encountered by my colleagues earlier than this level. Different issues we’ve discovered is that simply because a product works nicely within the laboratory setting in a Petri dish, it doesn’t imply that success will translate to the sector (Shock, shock!). Environmental circumstances can be a consider figuring out the effectiveness of a product – for instance, the entomopathogenic fungi examined labored pretty nicely in a moist Florida atmosphere however not a lot within the very dry Northern California. Dosage, product stability and software strategies are one other side of the product improvement that decide its success. As we all know, beekeepers are busy individuals and a product that’s fast and straightforward to throw inside a colony with out the necessity for frequent reapplication is a should! Nevertheless it takes a substantial effort to perform this. Contemplating all of this, I’m grateful that we’ve even the few merchandise obtainable to us. Regardless of the challenges, these had been very helpful experiences that may assist enhance the long run product improvement. And sure, one of many evaluated reformulated merchandise made it to the market, so I’m going to think about {that a} win.
Along with varroacides, beekeepers and researchers are very invested in breeding pest (and pathogen) resistant/tolerant honey bee traces as a long-term, extra sustainable resolution for managing pests and pathogens. As a result of I’ve been requested this query many instances, right here is your reply prematurely. Merely acknowledged, tolerance implies that the organism (on this case a honey bee) has developed various mechanisms permitting it to succeed regardless of the presence of a selected stressor, whereas resistance implies that the organism has developed mechanisms to maintain the stressor at low or no ranges. Over time, there have been quite a lot of breeding applications which have succeeded in creating completely different traces of honey bees obtainable to the beekeeping business. These completely different traces have been chosen for traits interesting to beekeepers together with pest, pathogen tolerance/resistance, fast early Spring construct up, Winter hardiness, gentleness and in some circumstances even colour, and many others. Nevertheless, there was a scarcity of direct comparability and characterization of those shares inside completely different environments. My doctoral scholar Lauren Gregory Rusert, is inquisitive about addressing this explicit query so as to have the ability to make higher suggestions to beekeepers primarily based on their very own operational pursuits and targets. Over the previous few years she evaluated six completely different honey bee shares for his or her efficiency by way of productiveness, pest and pathogen ranges and survivorship inside Northern California apiaries. She is at the moment writing a last manuscript from this venture, however in abstract her information reveal that whereas most shares have managed to maintain varroa mites considerably in test, there have been a pair that carried out a bit higher. Nevertheless, the mite stress in our space has been very excessive that sooner or later even one of the best performing shares wanted assist from the miticides. Keep tuned for the remainder of the story as Lauren is working exhausting to publish this information very quickly, and use the data for sensible incorporation in apiary operations primarily based on the wants of particular beekeepers.
Vitamin
Throughout the previous few years, I additionally initiated analysis in areas very new to my lab group, however extremely helpful to related stakeholder teams. These initiatives have an overarching theme of serving to to mitigate points dealing with managed honey bees by bettering diet. I’ve been lucky sufficient to companion with some fantastic and artistic collaborators from my very own College (Dr. Neal Williams, you should have a possibility to examine the entire superb analysis carried out in his laboratory within the upcoming problems with Bee Tradition!), different universities (Dr. Gregor Reid, The College of Western Ontario and Dr. Brendan Daisley, at the moment at College of Guelph) and USDA-ARS (Dr. Arathi Seshadri)

Analysis colonies in almond orchards with a mounted pollen lure to establish vegetation the bees foraged on (almonds versus supplemental forage)
As we very nicely perceive now, one of the best diet is offered by the pure forage that the bees can entry whereas out on their foraging journeys. The very first examine regarding diet evaluated two completely different supplemental forage plantings (mustard combine by Venture Apis m and wildflower combine developed by the Williams lab group) for his or her affect on brief and long-term colony well being and survival. Almonds in California bloom early within the 12 months, round mid-February, when there’s not a lot else round for bees to eat, however we all know that the varied dietary sources have advantages for bee well being. This is the reason there was a terrific push by researchers, beekeepers and non-profit organizations to include supplemental forage plantings inside or on the borders of almond orchards. Regardless of some climate challenges, we accomplished two years of the venture. Our outcomes additional affirm that the proximate good thing about supplemental forage is the improved development of the colony by improved brood manufacturing and due to this fact greater grownup workforce. On this venture, we didn’t affirm the affect on almond yield, nonetheless, we are able to postulate that elevated brood manufacturing results in elevated foraging and due to this fact probably elevated pollination effectivity. Curiously, and maybe most related to the beekeepers, our outcomes counsel that entry to supplemental forage has long-term advantages for colony measurement and survival with colonies having greater total variety of frames of bees going into Winter when getting access to particularly mustard plantings throughout almond bloom. We’re at the moment engaged on this manuscript so ensure that to look us up on Google Scholar. All of our analysis articles are revealed as Open Entry so that you shouldn’t have to pay to learn our analysis findings!

Employees evaluating colonies for the venture testing probiotics affect on colony well being.
Regardless of all the advantages of pure forage, habitat degradation, local weather change and decreased entry to pure areas, make it so the beekeepers as a rule have to offer supplemental feed to make sure colony survival. Whereas macronutrients, akin to proteins and carbohydrates, are the principle focus, beekeepers are searching for to offer a extra full diet by way of dietary supplements akin to probiotics or phytochemicals. Drs. Reid and Daisley have developed a probiotic complement (a 3 Lactobacillus spp. advanced) that has proven to suppress Paenibacillus larvae, the causative agent of American Foulbrood within the laboratory and preliminary area research. Naturally, we wished to check the affect of this probiotic complement on total colony well being and productiveness, when utilized both by way of protein patty or sprayed straight on brood frames. Our outcomes counsel that probiotics used inside a protein complement improve colony energy and honey manufacturing and cut back an an infection with Nosema spp. as in comparison with pollen patty alone. Curiously, we discovered that software by way of spray has an affect on bacterial and fungal communities throughout the uncovered bees with potential inhibitive implications for identified honey bee pathogens. This work has been revealed and if you need to be taught extra about it, I invite you to go to: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41396-023-01422-z. A reasonably cool aspect notice, whereas processing the samples for this venture, Dr. Daisley recognized a novel bacterial genus throughout the honey bee intestine. The manuscript has been submitted for publication so keep looking out.

Caged bees fed phytochemcials and noticed for survival and hypopharyngeal gland improvement.
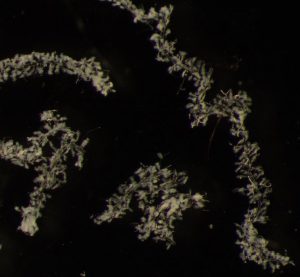
Underdeveloped hypopharyngeal glands from bees within the phytochemicals experiment. Photograph by S. Yokota.
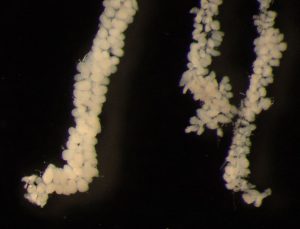
Properly developed hypopharyngeal glands from bees within the phytochemicals experiment. Photograph by S. Yokota.
Together with probiotics, the usage of phytochemicals to enhance colony well being has garnered consideration from beekeepers. Whereas the identify sounds intimidating, phytochemicals are merely compounds naturally produced by vegetation and often garner some form of safety to the plant. These are collected by bees when foraging on pollen and nectar. My collaborator Dr. Arathi (USDA-ARS) has reported on the advantages of a number of of those phytochemicals on Nosema hundreds and bee survivorship in cages. We then wished to guage a number of phytochemicals (caffeine, p-coumaric acid, gallic acid and kaempferol) for his or her affect on bee’s physiological parameters. We discovered that in a cage examine, younger employee bees when offered particularly p-coumaric acid had bigger hypopharyngeal glands which produce secretions used to feed creating brood. You possibly can learn extra about this analysis right here: https://www.cell.com/heliyon/pdf/S2405-8440(22)01740-6.pdf. Our information lead us to assume that a few of these phytochemicals have the potential to enhance colony development and productiveness, significantly throughout irritating instances. However, as we discovered earlier than, simply because one thing is efficient in a lab, doesn’t imply it is going to work within the area. A pilot area examine did counsel that a few of these compounds would possibly enhance colony longevity. Presently, we’re increasing this venture to raised perceive the potential worth of those phytochemicals as a feed complement. The sphere venture is ongoing and is led by Richard Martinez, a Masters scholar in my lab.
I can’t end this text with out acknowledging the various funding sources supporting this work together with USDA, USDA-ARS, Venture Apis m, California State Beekeepers Affiliation and lots of non-public donors. And everyone knows that the work wouldn’t be carried out with out the dedication of many glorious college students, lab assistant, postdocs and volunteers (Thanks all!). And for these studying, please come again to be taught extra about our analysis in Half 2!
[ad_2]